Healthcare Data Analytics: Overcoming Obstacles with FHIR
Introduction
The worldwide big data healthcare market grew to $22.73 billion in 2023, with a notable compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.9%. It is anticipated to reach $53.96 billion by 2027, with a projected CAGR of 24.1%. We are here to provide insights into the prospects and obstacles of utilizing data analytics in the field of healthcare. Let's get started!
Dealing with extensive volumes of data in the healthcare sector poses significant challenges. Despite the increasing input of patient information into electronic health records (EHRs), a substantial portion remains untapped or leads to less streamlined workflows. Healthcare analytics tools emerge as pivotal solutions in harnessing this data, empowering healthcare systems to enhance patient results, base decisions on data insights, and obtain a comprehensive overview of population health.

Though data analytics holds immense promise in healthcare, gathering and effectively utilizing healthcare data presents a range of difficulties. This blog delves into both the prospects and hurdles surrounding data analytics in the healthcare sector, as well as the strategies being devised to tackle them.
RELATED: Clinical Decision Support Systems: Revolutionizing Healthcare Decision Support
Big Data in Healthcare – What's Its Significance?
Big data in the healthcare sector encompasses the extensive collection of data through digital technologies, facilitating the more effective management of patient records and hospital operations.
While big data provides a vast repository of information, data analytics plays a crucial role in extracting insights and patterns from this data to enhance both patient care and operational effectiveness.
Leveraging data analytics opens up possibilities for preventing outbreaks, reducing expenses, and elevating the quality of patient care.
Furthermore, the integration of data from diverse sources, such as patient portals, electronic health records (EHRs), Telemedicine software, wearable devices, and government agencies, presents challenges. Nevertheless, advancements in technology enable more streamlined data gathering and analysis, ultimately leading to proactive issue resolution and improved healthcare delivery.
The Challenges of Healthcare Data Analytics in Healthcare and Solutions
Data Structure Issues
Healthcare encounters issues with data structure. unstructured data in healthcare lacks a defined format in its original state. The majority of healthcare data is unstructured, accounting for approximately 80% of the total data volume. This is primarily due to the significant presence of medical imaging data, making up 80% of clinical content, as noted by NetApp. For instance, a single chest X-ray can be about 15 megabytes in size, whereas a 3D mammogram may reach 300 megabytes, and a digital pathology file can be as large as 3 gigabytes, roughly equivalent to the size of a high-definition full-length movie.
The lack of interoperability in electronic health records (EHRs) exacerbates this problem, hindering the sharing and examination of data. Consequently, unstructured data forms a substantial obstacle for healthcare practitioners aiming to harness data analytics for enhancing patient outcomes and operational efficiency in healthcare
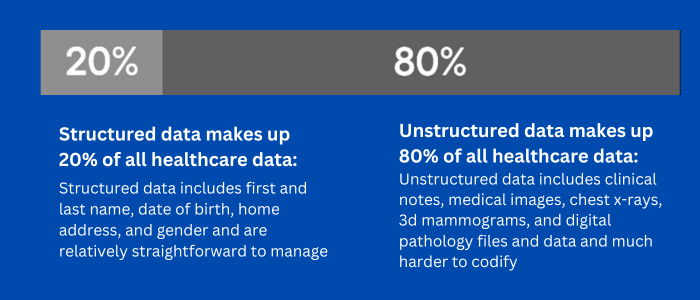
Solution: To address the challenge of unstructured healthcare data, advanced technologies such as natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning can be employed to extract and structure information from textual narratives. For medical images, the use of image analysis and recognition algorithms can help organize and interpret visual data.
RELATED: How can EHRs like Epic, Cerner, and MEDITECH be Integrated Cost Effectively
Data Disparity
In healthcare, electronic medical record (EMR) data can be incomplete due to either inadequate data collection or inadequate documentation. Insufficient data collection happens when specific medical aspects are not assessed in patients.
Notably, around 80% of significant medical errors stem from communication issues during transitions in patient care, especially when moving to different care settings. Some datasets, like updates on patients' vital signs, require regular intervals for updates, while others, such as place of residence or marital status, change only infrequently in a person's lifetime. It's essential for healthcare providers to distinguish between data that necessitates manual updates and data that should be updated automatically to prevent disruptions for end-users and uphold data quality.
Recognizing the unpredictability of data changes can pose challenges for organizations that don't consistently monitor their data assets. It's important to avoid creating unnecessary duplicate records during updates, as this can impede clinicians' access to critical patient information for making patient-centered decisions.

Solution: Fortunately, there are various techniques available to address the issue of missing data and sparsity, such as imputation methods. These approaches can be classified into two categories: those assuming that missing data are randomly distributed, encompassing straightforward methods like mean imputation and more sophisticated techniques like maximum likelihood and multiple imputations, and those assuming that missing data are not random, such as selection models and pattern-mixture models.
Data Privacy & Security
Healthcare data faces numerous security threats, ranging from phishing attacks and malware to the risk of physical loss, like laptops left in public places. Safeguarding patient information, as mandated by HIPAA, involves protecting the nearly 18 components of protected health information (PHI). The challenge is to maintain data value for analysis while eliminating these core PHI elements. The HIPAA Security Rule prescribes a range of technical security measures for organizations handling PHI, encompassing authentication protocols, data transmission security, access controls, auditing, and more. While many organizations implement security measures like antivirus software, data encryption, and multi-factor authentication, even well-protected data can be compromised due to complex challenges related to data and software access.
Solution: To address the challenges of data privacy and security in healthcare, organizations can take several essential steps. First and foremost, robust data encryption should be implemented to safeguard sensitive patient information, ensuring that even if data is compromised, it remains indecipherable. Regular auditing of data access and usage is crucial to monitor and identify potential breaches. Comprehensive staff training on security best practices helps mitigate the risk of human error and enhances overall awareness. Strict compliance with HIPAA regulations and guidelines is paramount. Data loss prevention (DLP) solutions can be employed to prevent accidental data exposure, and continuous security monitoring should be in place to detect and respond to suspicious activities and potential threats promptly.RELATED: Tips for Securing Private Health Data in Healthcare Cyber security
Lack Of Standardization
In the healthcare sector, electronic health record (EHR) systems are the common tools for storing and exchanging patient data within an organization's network. However, the absence of uniformity and compatibility among EHR platforms, both internally and externally, presents a substantial obstacle for effective data analytics.
Data being stored in non-homogeneous formats and the lack of standardization complicates the processes of data acquisition and cleansing. These difficulties lead to restricted interoperability, a major hurdle for healthcare data analytics. Since data is seldom standardized, there are challenges in obtaining and preparing data in a consistent format that allows for universal sharing and analysis. As data becomes more globally integrated, the field of data analytics must address barriers including language differences, diverse standards, and varying terminologies.
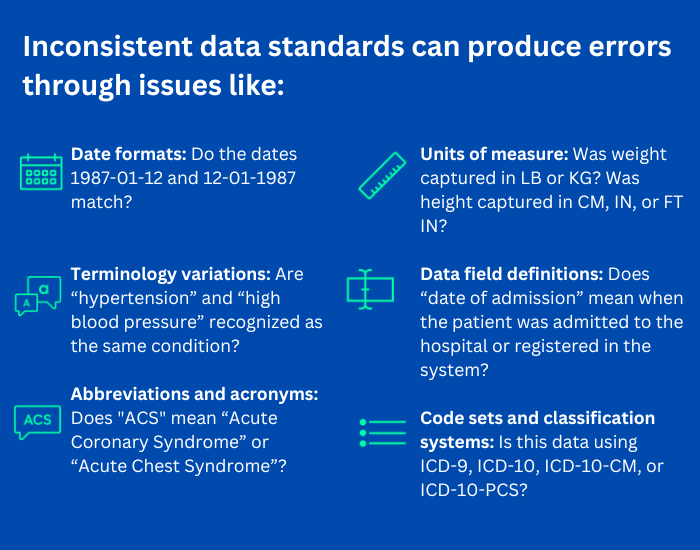
Solution: To combat the issue of data standardization in healthcare, several standards development organizations, such as Health Level Seven International (HL7), have devised standards to facilitate global health data interoperability. Standards like FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources), a highly adopted HL7 standard, hold the potential to establish a unified data standard across healthcare organizations, ultimately resolving data standardization challenges.
RELATED: Standards & Regulations for Healthcare IT Services and Software development
Data Storage and Transfer
Generating data is cost-effective in comparison to the expenses involved in storing and transferring it. Securing and maintaining generated data comes with significant costs. Additionally, there are expenses associated with moving data from one location to another, as well as the analytical process.
Certain researchers have integrated considerations of data structure, storage, and transfers. They demonstrate how structured data can be readily stored, queried, and analyzed, while unstructured data poses more challenges in manipulation. Cloud-based health information technology introduces an extra layer of security in managing patient-related data during extraction, transformation, and loading processes. The utilization of data analytics must grapple with issues surrounding rising costs and the secure transmission of information.
Solution: To address the challenge of high costs associated with securing, storing, and transferring healthcare data, organizations can consider optimizing data storage and management through cloud-based health information technology solutions, which offer cost-effective scalability and enhanced security. Additionally, implementing efficient data analytics practices can help manage expenses while ensuring the secure transmission of information, thus addressing financial and data security concerns.How FHIR can help overcome Challenges?
- Data Standardization: FHIR provides a standardized framework for structuring healthcare data, making it easier to exchange and analyze information.
- Interoperability: FHIR integration enables seamless data sharing between different healthcare systems, improving the accessibility and integration of data.
- Real-time Data Access: FHIR supports real-time access to patient data, facilitating timely analytics and decision-making.
- API Integration: FHIR's API capabilities allow for efficient data retrieval and interaction with EHRs and other healthcare applications.
- Patient-Centric Data: FHIR emphasizes a patient-centric approach, allowing analytics to focus on improving individual patient outcomes.
- Scalability: FHIR's scalable architecture accommodates the growing volume of healthcare data, supporting evolving analytics needs.
RELATED: FHIR Implementation for Interoperability Success in Healthcare
Here are some specific examples of how FHIR is being used to overcome challenges to implement data analytics in healthcare:
- The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is using FHIR to develop a new clinical data warehouse that will integrate data from a variety of sources, including EHRs, medical devices, and patient portals. The data warehouse will be used to develop clinical decision support tools and improve patient safety.
- The University of California, San Francisco (UCSF)is using FHIR to develop a new data analytics platform that will be used to generate insights from clinical data to improve patient care and operational efficiency.
- The American Heart Association (AHA)is using FHIR to develop a new data sharing platform that will make it easier for researchers to access and share clinical data from different sources. This will help to accelerate research into new treatments and cures for heart disease.
Conclusion
Data analytics plays a crucial role in healthcare by enhancing the ability of healthcare providers to offer personalized and effective patient care and by identifying and addressing emerging health trends and challenges. FHIR is a powerful tool that can help healthcare organizations to overcome challenges to implement data analytics.
If you are ready to take your data analytics to the next level, contact our team of Healthcare IT experts today. We can help you with FHIR Integration and realize the full potential of intelligent data to improve patient care.





